The MAIN JOURNAL for POWER GRID SPECIALISTS in RUSSIA
3 - 6 J U N E 2 0 1 9
MADRID, SPAIN

28
Th
e Functionality of Monitoring
Systems under Transforming
Power Grid of Active Сonsumers
Andrey KUCHERIAVENKOV,
Director of ANTRAKS R&D LLC
Ekaterina KARTASHEVA,
Head of marketing department, Trinity Engineering LLC
T
he current transformation
of power system towards
a decentralized model
brings some features in
the changing power supply from
the practice of complex distribu-
tion networks. The presence of
prosumers in the grid and the
need to integrate renewable en-
ergy sources require a dynamic
change in the transmission and
distribution of electricity. The key
features of new generation net-
works are power lines operation
with alternating feed from differ-
ent directions and smart control
of power system facilities, which
require not ordinary maintenance,
but a quick response to the state
of power equipment.
For simple configuration and
reconfiguration of the upgraded
power grid, automation level in-
crease in the field of observabil-
ity and controllability of all power
system components in real time
is needed. The calculation of net-
work automation points, support
of self-restorability functions, dy-
namic voltage regulation and load
reduction require continuous mon-
itoring of power lines and equip-
ment, as well as self-diagnostics
of monitoring and control de vices.
As of today, existing modern
software and hardware systems
process information from vari-
ous data sources simultaneously,
compare the received informa-
tion with accumulated database
of network performance and use
a probabilistic model and artificial
intelligence mechanisms for cut-
ting off false data and assessing
risks and management decisions
respectively. These software and
hardware systems increase the
depth of diagnostic information
analysis significantly.
The use of geographic infor-
mation systems, including infor-
mation about the location and
properties of three-dimensional
objects in the coordinate-time
system, provide maximum visi-
bility and usability of upgraded
networks monitoring. Using the
geographic information system it
is possible to form a multi-level in-
formation network and monitoring
and control systems for overhead
and cable lines based on the data
from various diagnostic devices:
current sensors, voltage sensors,
power line temperature sensors,
icing sensors, three-dimensional
position sensors of the conductor,
topographic and remote devices
for determining power line dam-
age location. These data will not
only provide immediate response
to events in the power system,
but also create the conditions for
implementing predictive damage
diagnosis mechanism, assessing
the probability of individual net-
work nodes failure and moving on
to active adaptive configuration of
distribution networks.
The basic functionality of the
monitoring system is the cor-
rect identification of all power
lines damages (single-phase-to-
ground faults and phase-to-phase
faults), when taking place any
direction of power flow or zero
power flow (line under guard volt-
age), wire breakage, automatic re-
closing or damages, occurring in
normal operation, and when con-
necting consumers to distribution
network. Determination of dam-
age location with visualization of
the current network state and the
accident place, power lines auto-
matic sectioning during an emer-
gency process and accounting for
unserved electricity are ensured
by the implementation of a geo-
graphic information system for
monitoring and controlling power
transmission.
The monitoring and automation
system of the distribution network,
offered by ANTRAKS, is based on
the use of intelligent sensors of its
own design and production (short-
circuit indicators for overhead
lines, A-signal electrical network
monitors, smart digital discon-
nectors). The system allows en-
gineers to identify any accidents
on 6-110 kV overhead and cable
lines, as well as promptly sec-
tionalize damaged areas. In ad-
dition, the system predicts some
emergencies in advance based
on the analysis of overhead lines
equipment. When scaling up the
analytical part, the system allows
engineers to manage information
and business analytics based on
digital technologies for process-
ing large data arrays using artifi-
cial intelligence systems and ma-
chine learning.
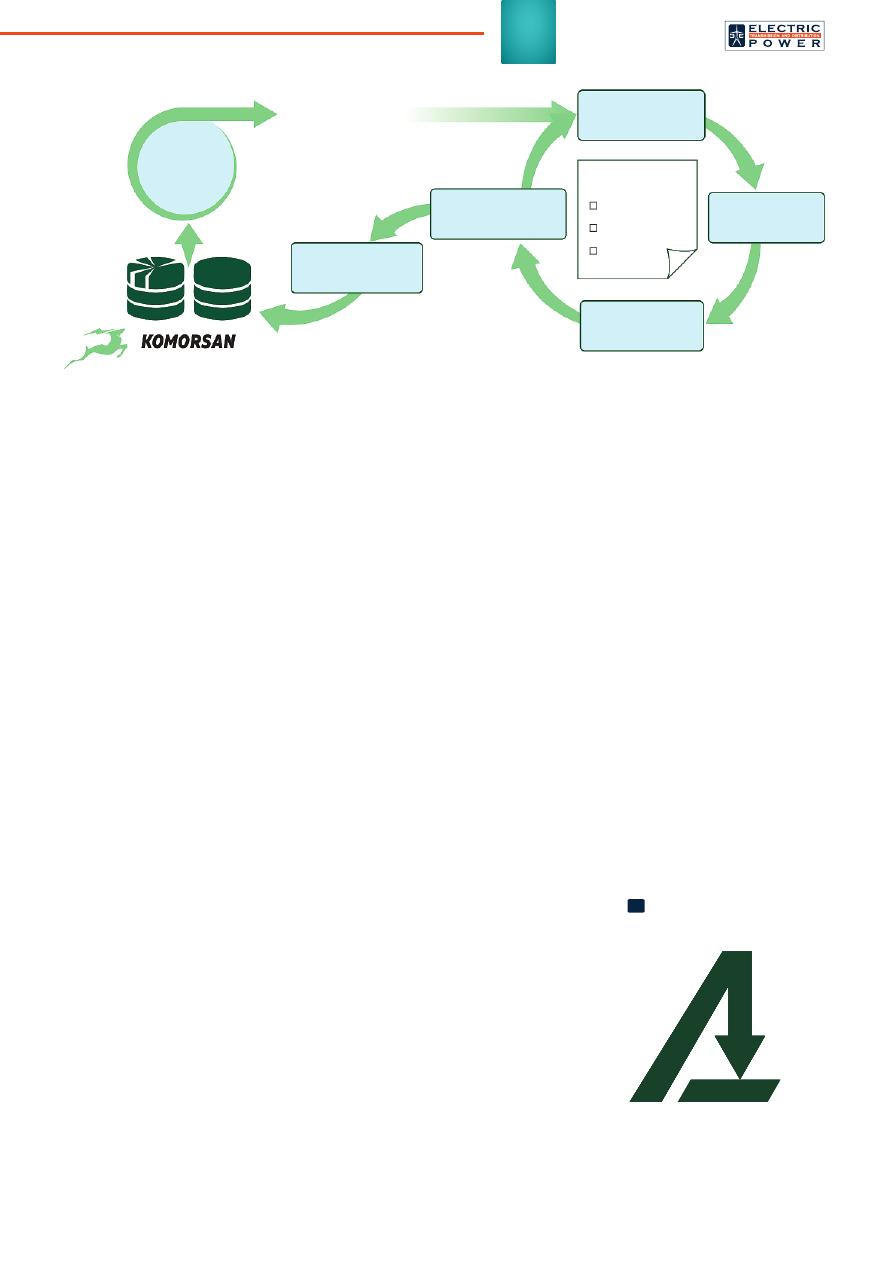
The central part of the system
is the KOMORSAN data acquisi-
tion and processing server. Data
from smart sensors is sent to the
server via different communica-
tion channels, depending on the
INN
OVAT
I
O
N
S A
N
D
EFF
I
C
I
E
N
CY PROPOSALS
29
types of devices included in the
system. Instrument packages
equipped with a GSM module es-
tablish TCP/IP connection for data
exchange. Indicators, using a data
relay channel based on Mesh net-
work, transmit information to the
server via an intermediate data
acquisition controller, which is the
network coordinator and interface
converter. Information transfer to
the KOMORSAN system takes
place in real time. The flexibil-
ity of KOMORSAN system data
model allows engineers to man-
age a set of roles and privileges
as well as login level of users in
the KOMORSAN Web client. The
system has built-in cyber security
mechanisms and stores informa-
tion about user actions.
The system is optimal for moni-
toring 6-110 kV overhead and ca-
ble lines due to the high sensitivity
of devices. Registration of emer-
gency currents from 0.5 A and
implementation of several emer-
gency detection algorithms guar-
antee the absence of false alarms
at low emergency currents and
reliable determination of all emer-
gencies (single-phase-to-ground
faults and phase-to-phase faults).
Determining the direction of short
circuit current makes it possible
to locate damaged overhead line
section and exact distance to the
fault.
The monitoring system does
not require the installation of ad-
ditional equipment at substations
(it reduces the overall cost of the
system), complex erecting work at
substations and creation of arti-
ficial modes with current surges,
reducing the service life of net-
work equipment. Synchronous
voltage and currents measure-
ments in each phase with real-
time stamp and construction of
oscillograms and vector diagrams
for each phase make it possible to
verify the correct power line phas-
ing and to monitor the processes
in real time for transiting to risk-
oriented network management.
ANTRAKS smart sensors are
made in plug-and-play technology
and do not require user custom-
ization. The use of controlled de-
vices for power system sectioning
increases power equipment life-
time, as opposed to vacuum cir-
cuit breakers (reclosers), generat-
ing high-frequency (50-200 kHz)
overvoltage in electrical networks
and leading to premature failure
of transformers.
T h e s y s t e m o f f e r e d b y
ANTRAKS is cross functional. It
is integrated with existing infra-
structure of distribution networks,
including SCADA systems. Also it
provides the possibility to control
power districts when connecting
sectionalizing devices. The sys-
tem is easily customizable: it is
possible to switch on mimic dia-
grams, to add allocation of dam-
aged area, to point out additional
user roles and to collect analyt-
ics in a convenient form. Moni-
toring provides an opportunity to
increase power line transmission
capacity.
The system allows engineers
to control peak loads. It is espe-
cially important when integrating
renewable energy sources and
active consumers. The system is
capable to make independent de-
cisions, including the control of
power flow. The use of probabilis-
tic algorithms and machine learn-
ing algorithms ensures fault toler-
ance of the system as well as its
self-diagnosis and self-learning.
The phased implementation of an
integrated system is very conve-
nient economically, the system
is easily scaled "in width" (geo-
graphically) and "in depth" (con-
nection of new devices).
An integrated approach to
electrical network monitoring pro-
vides a simple solution for the
problem of upgrading and im-
proving power system reliability.
Using the achievements of mod-
ern electronics, communication
systems and machine learning
technologies makes it possible to
cost-effectively solve the problem
of quick power restoration with-
out installing primary equipment
and changing the network topo-
logy.
Р
Diagnostics
Risk
determination
Modernization
Reconfi guration
Monitoring
Planning
Analysis
and prioritization
Risk list
Main risks
Database
ANTRAKS R&D, LLC
+7 (495) 991-12-30,
www.antraks.ru,
offi
ce@antraks.ru
24th World Energy Congress
Special issue, September 2019
Оригинал статьи: The Functionality of Monitoring Systems under Transforming Power Grid of Active Сonsumers
The current transformation of power system towards a decentralized model brings some features in the changing power supply from the practice of complex distribution networks. The presence of prosumers in the grid and the need to integrate renewable energy sources require a dynamic change in the transmission and distribution of electricity. The key features of new generation networks are power lines operation with alternating feed from different directions and smart control of power system facilities, which require not ordinary maintenance, but a quick response to the state of power equipment.