The MAIN JOURNAL for POWER GRID SPECIALISTS in RUSSIA

56
SUN GOES
FROM THE EAST
Green energy
The Far East of Russia has become a leader in terms of renewable energy
innovations. This is where renewable energy projects have become economically
justi
fi
ed today. A long distance between a large number of populated localities
and the Uni
fi
ed Power System, as well as the complexity and high price of energy
delivery create a huge potential for the optimization of the Far East power
engineering by means of adoption of renewable energy technologies.
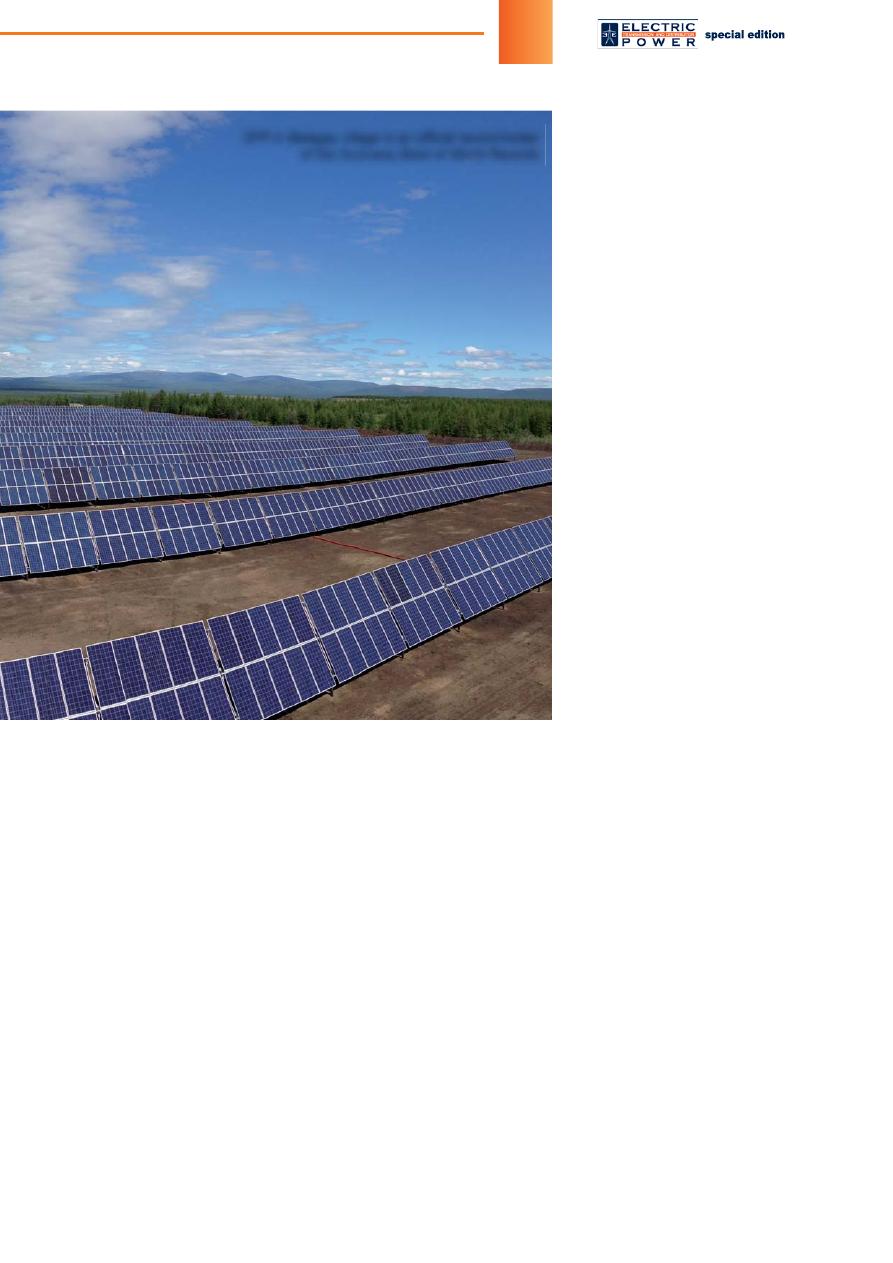
Thirteen solar power plants
(hereinafter – SPP) including the
northernmost one in the world
(Batagayskaya SPP) have been
put into operation on the Republic
of Sakha (Yakutia) territory for the
last
fi
ve years. Other three SPP
will be building in 2016. Wind-dri-
ven power plants operate success-
fully in the Kamchatka Region and
the Sakhalin Region. Neverthe-
less, major changes will happen
in the industry. According to the
Holding “RAO Energy Systems of
the East” estimates, the construc-
tion of solar and wind power gene-
ration is feasible for 178 populated
localities of the Far East. Renew-
able energy facilities total capacity
may be more than 146 MW.

57
Fuel Saving
In addition to the major power
plants, electrical grids and heating
networks, the Holding “RAO Ener-
gy Systems of the East” also
operates more than 185 diesel
power plants (hereinafter – DPP),
which are located throughout the
Far Eastern Federal District in the
decentralized power supply areas.
The replacement of DPP on the
wind-driven power plants or solar
panels is a necessary solution.
Diesel generators, which are worn-
out and obsolete in a majority,
require regular fuel transportation.
It is necessary to provide fuel
reserve for the hundreds of
populated localities surrounded
by cold desert or boreal forest
every year. The fuel reserve must
be suf
fi
cient for use during heating
season. Many settlements have
a connection with supply centers
by means of land transport or
water transport for the short time.
That connection is possible during
the river navigation period or by
using roads which appear on the
frozen rivers and bogs territories.
Power engineers and authorities
often put a lot of efforts in order
to provide suf
fi
cient amount of
fuel. Sometimes, transportation
of cargo to the remote areas of
Yakutia and Kamchatka requires
to use several mode of transport
and takes two or three years.
Due to high transportation ex-
penses and ineffective equipment
operation in the remote areas of
the Far East the prime cost for
1 kW•h can reach 100 rubles. The
fuel is a half of the prime cost. By
reason of the fact that the diesel
price becomes higher the regions
are forced to increase tariff sub-
sidies.
The implementation of alter-
native energy sources has not al-
lowed to abandon DPP com-
pletely, but it has already pro-
vided signi
fi
cant fuel saving. The
Holding “RAO Energy Systems of
the East” designs a lot of renew-
able energy facilities assuming
that it will replace up to 40 % of
electricity produced by DPP. As
a result of fuel saving power en-
gineers can get money and return
investment in the purchase, deliv-
ery and setup of new equipment.
After the end of the pay-off period
due to fuel saving it will possible
to stabilize and even reduce tariff.
Renewable energy develop-
ment in the Far East creates
a real opportunity to improve the
quality of live for many people.
Wind-driven power plants and
SPP in the isolated settlements
are not environmental protection
or desire to reduce carbon dioxide
emission. For such populated
localities renewable energy is the
way to save expensive imported
fuel and provide free access to the
electricity all day and night.
Pioneers of
Renewable
Energy
People from the remote set-
tlement of Batamay, which is cut
off by river from the central infra-
structure, remember very well that
electricity is a bene
fi
t of civiliza-
tion. “I was six or seven years,
when electricity appeared in our
little village. Electricity was avail-
able one day per week (in Satur-
day from 6 to 11 p.m.). That day
was a holiday for us. Now, of
course, the situation is different.
We have a possibility to use elec-
tricity permanently. Furthermore,
new technologies have come to
us. Our SPP is a matter of pride.
At
fi
rst, the interest and curiosity of
the local population was very high.
People came to observe the con-
struction process and asked the
questions”, the autonomous DPP
machinist of Batamay, Andrey
Berezovsky told.
PJSC “RAO Energy Systems
of the East” and second-tier sub-
sidiary PJSC “Sakhaenergo” de-
SPP in Batagay village is an of
fi
cial record-holder
of the Guinness Book of World Records

58
cided to build the
fi
rst experimental
SPP in Batamay four years ago.
“When the decision to build in
Batamay the
fi
rst SPP in Yakutia
was made, we were glad, because
it was a new project for us and
for the village residents. We did
not have experience of operation
with such technologies, but as the
phrase goes: what the eye fears,
the hands do”, the autonomous
DPP of Batamay chief, Vasily Pro-
todyakonov told about his native
village. Initially, the SPP consisted
of 52 solar panels with total elec-
tric capacity of 10 kW. The photo-
electric array was placed near the
existing DPP. Economic bene
fi
t
from new technologies became
obvious pretty soon. After a year
the specialists of “Sakhaenergo”
have increased capacity of Bata-
may SPP up to 30 kW. However,
the modernization of the SPP has
not stopped yet. Power engineers
decided to increase electric capa-
city by 30 kW in 2014. Currently
the SPP produces 60 kW. The
com pany’s investments helped to
create multifunctional autonomous
energy complex in the village,
which consisted of automated DPP
with electric capacity of 160 kW,
SPP with electric capacity of 60 kW
and energy storage system with
available capacity of 86,4 kW•h.
Electricity from the SPP reduces
equipment deterioration, decreas-
es village dependence from sea-
sonal diesel fuel supply and allows
to save money.
Power engineers serves solar
panels regularly in order to keep it
during all life cycle. They remove
dust from the surface of solar
panels by means of special brush
in summer and remove snow in
winter.
Caught Wind
The experiment was success-
ful because the SPP brought sig-
ni
fi
cant economic bene
fi
t and did
not fall out during the winter frosts.
Besides power engineers found
suitable solutions for SPP con-
struction in the northern climate
and knew about requirements to
the equipment. After experience
of Batamay others remote popu-
lated localities of the Republic of
Sakha (Yakutia) began to develop
solar power systems. Solar power
plants with electric capacity from
10 to 1000 kW appeared in 13 set-
tlements in the next four years.
At the same time the Holding
“RAO Energy Systems of the East”
began to develop wind power in
the Kamchatka Region. The
fi
rst
project appeared in the most re-
mote corner of the region (on the
Commander Islands) by efforts of
PJSC “Mobile Energy”. People
often call that archipelago as “Is-
land of winds and fog” or “Island
of everlasting autumn”. Cold oce-
anic current from the north faced
there warm southern current. As
a result there are mild winter for
the northern latitudes, cool, rainy
summer, strong winds and storms
all the year round. It is unlikely that
someone likes such climate, but
that environmental conditions were
ideal to start to use wind energy
into the local power supply sys-
tem. Erection of two new French
wind-driven power plants, which
were combined with diesel genera-
tors and small boiler room, was
fi
-
nished close to Nikolskoye village
(the only populated locali ty on the
Bering Island and the archipelago)
in June 2013. Union of wind-driven
power plants, diesel generators
and small boiler is necessary in the
remote isolated power systems.
Extra wind energy is converted into
heat in the wind-diesel power plant
(electric heating tubes of the boiler
participate in the village heating
during strong wind), and when
wind is insuf
fi
ciently strong, DPP
provides power supply of the load.
For extra energy storage it is
possible to use storage batteries
but the price of such batteries is
pretty high. But conversion of ex-
tra energy to heat is a cheap and
practicable solution for the north-
ern latitudes.
Bering Island became an ex-
cellent test for “Mobile Energy”
project team. As a result, “Mobile
Energy” staff received experience
of the equipment setup and oper-
ation taking into account climatic
and geographical environment of
the region.
The First
Megawatts
The next step of renewable
energy development in the Far
East was implementation of large-
scale projects. The
fi
rst time PJSC
“RAO Energy Systems of the
East” began to construct SPP with
electric capacity more than 1 MW
in Batagay village (regional center
of the Verkhoyansk nomad camp)
in 2015. The SPP construction in
Batagay was a part of cooperation
agreement focused on renewable
energy development between
PJSC “RAO Energy Systems
of the East” and government of
the Republic of Sakha (Yakutia).
Bata gay was among the
fi
rst
worker’s settlements in Yakutia.
Many people consider that Bata-
gay makes a contribution in the
industrialization of the northern
region. Local residents needed
a reliable source of energy, which
would be able to reduce power
supply dependence of the village
from expensive fuel and replace
the only source of electric capa-
city – Batagayskaya DPP.
Harsh and cloudless winter in
Batagay takes eight months of the
Wind-diesel power
plant in Nikolskoye
village.
Power turbines
were equipped
with a lifting
gear on Bering
island

59
year, however insolation level is
almost the same as in the south-
ern Russia during spring and sum-
mer. Extreme climate of Yakutia
has high requirements for the SPP
equipment: it is able to operate un-
der the conditions of air tempera-
ture +40°C in summer and -45°C
in winter. The photoelectric array
consists of 3360 polycrystal pa-
nels “Suntech” with electric capac-
ity 300 W each. The SPP area is
almost 4 hectares. The life cycle
of the main equipment is 25 years.
The SPP equipment is adapted to
the climatic conditions of the polar
region. For example, photovoltaic
panels have a canting angle of
15 degrees in the Crimea. Such
angle in the north of Yakutia is
53 degrees. Moreover, piles are
erected there in the deep-frozen
soil.
The
fi
rst stage of SPP will pro-
duce about 1,2 million KW•h per
year. It will allow to reduce pur-
chase of diesel fuel for the village
by 300 tons per year and save
16 million rubles (at 2015 values).
More than 60 % of electricity
tariff in the village Batagay is a fuel
factor. Due to constant increase
of the diesel fuel prices electricity
generation becomes more expen-
sive as well.
“There are almost 4000 resi-
dents, nursery schools, hospitals,
educational facilities and enter-
prises in the village therefore it
is necessary to provide uninter-
rupted power supply there. Be-
sides new SPP will create reserve
of power, which increase electric
reliability of Batagay during maxi-
mum demand in autumn and win-
ter”, PJSC “RAO Energy Systems
of the East”, Deputy General Di-
rector, Alexey Kaplun explains.
Also he states that a positive
result was received due to a spe-
cial construction method, which
was used during the implemen-
tation of the project. According to
that method several facilities were
constructed at the same time (it is
important to note that all facilities
were located close to each other).
“The implementation of a major
project in Batagay allowed us to
reduce expenses on the construc-
tion low-power stations in the ad-
NATURAL POTENTIAL
OF THE FAR EAST
The Far East of Russia has unique potential in the
fi
eld
of renewable energy. There are strong wind along the coast-
line of the Arctic and Paci
fi
c Oceans, sunny weather on the
mainland, potential of rivers, tides and geothermal energy.
It can give hundreds gigawatt of power to provide the local
residents needs and to have an impact on economy and en-
vironment of the region. According to “RAO Energy Systems
of the East” estimates solar power plants and wind-driven
power plants can develop the most rapidly. Average annual
wind speed in the littoral villages of the Kamchatka Region is
6-7 m/s. It means a large potential for wind power engineer-
ing development and bene
fi
t for residents of the region. As
a comparison: average annual wind speed in Denmark (the
world leader in the
fi
eld of wind power engineering) is a little
more than 5 m/s. According to expert view wind potential
of Kamchatka coast may be more than 30 billion kW•h per
year. It signi
fi
cantly exceeds current power demand of the re-
gion. The sunniest region of Russia is the Primorsky region.
According to NASA DNI factor (level of solar irradiation) is
about 1700 kW•h per square meter per year, or 4.5 kW•h per
square meter per day there. As a comparison that factor is
less than 1500 kW•h per square meter per year in Krasnodar
region. The solar activity level varies from 700 to 1200 kW•h
per square meter per year in the majority of isolated settle-
ments of Yakutia. That level of solar activity may seem pretty
small. However, DNI factor is 0.9-1.1 thousand kW•h per
square meter per year in Germany, which is the world leader
in terms of installed capacity of solar power plants.
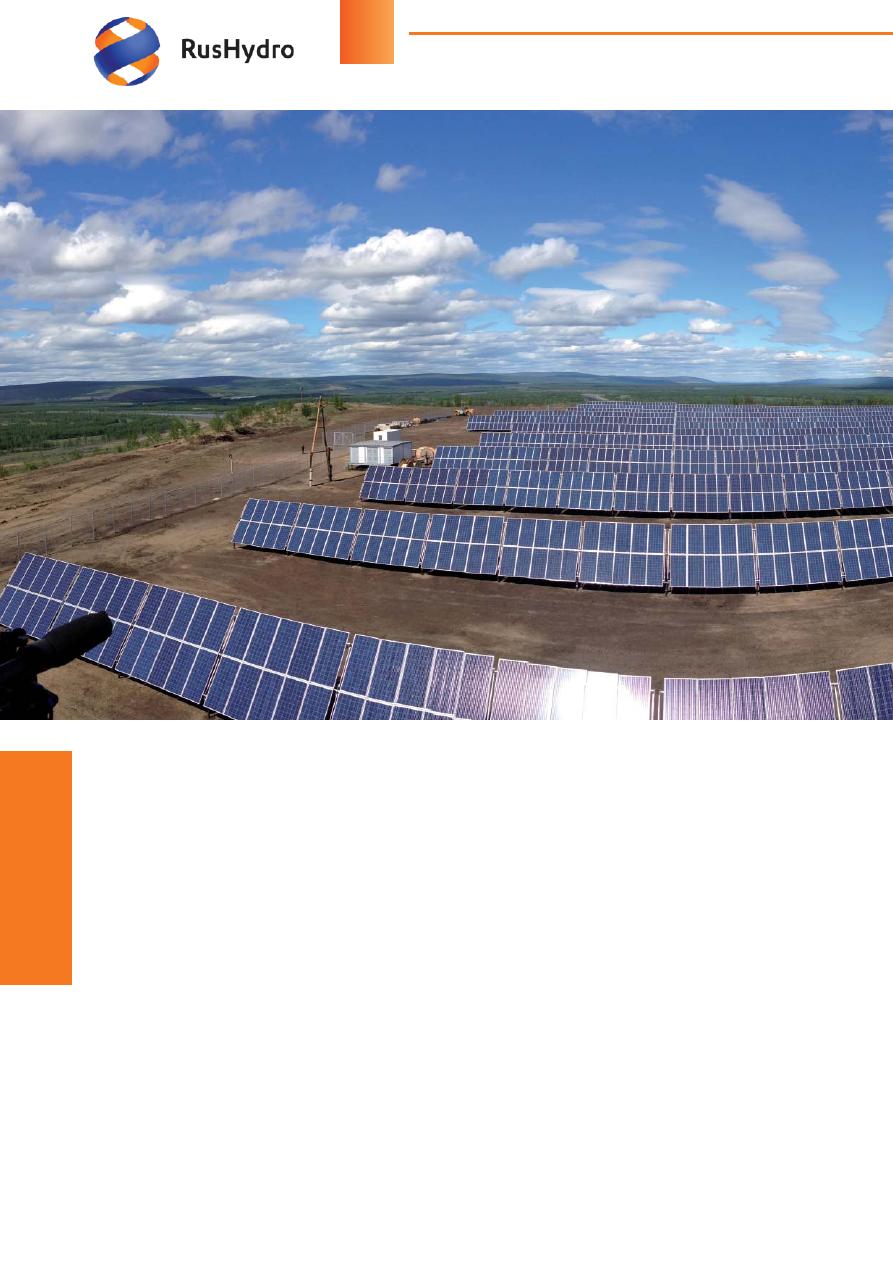
SPP in Batamay village.
Photovoltaic panels have a canting angle
of 55 degrees in the northern latitudes
R
e
n
e
w
a
b
le
en
er
g
y

60
jacent villages Betenkes and Stol-
by”, Alexey Kaplun says.
The synchronous operations
gave opportunities to make cen-
tralized purchasing and delivery
of the equipment and reduce
construction time and outlay cost
by means of effective use of the
hardware and labour resources.
Currently PJSC “RAO Energy
Systems of the East” considers
the possibility of implementation
of afore-mentioned SPP construc-
tion method (when several ad-
jacent SPP are built at the same
time) in Olekminsky, Ust-Jansky,
Verkhnekolymsky and Oimyakon-
sky regions.
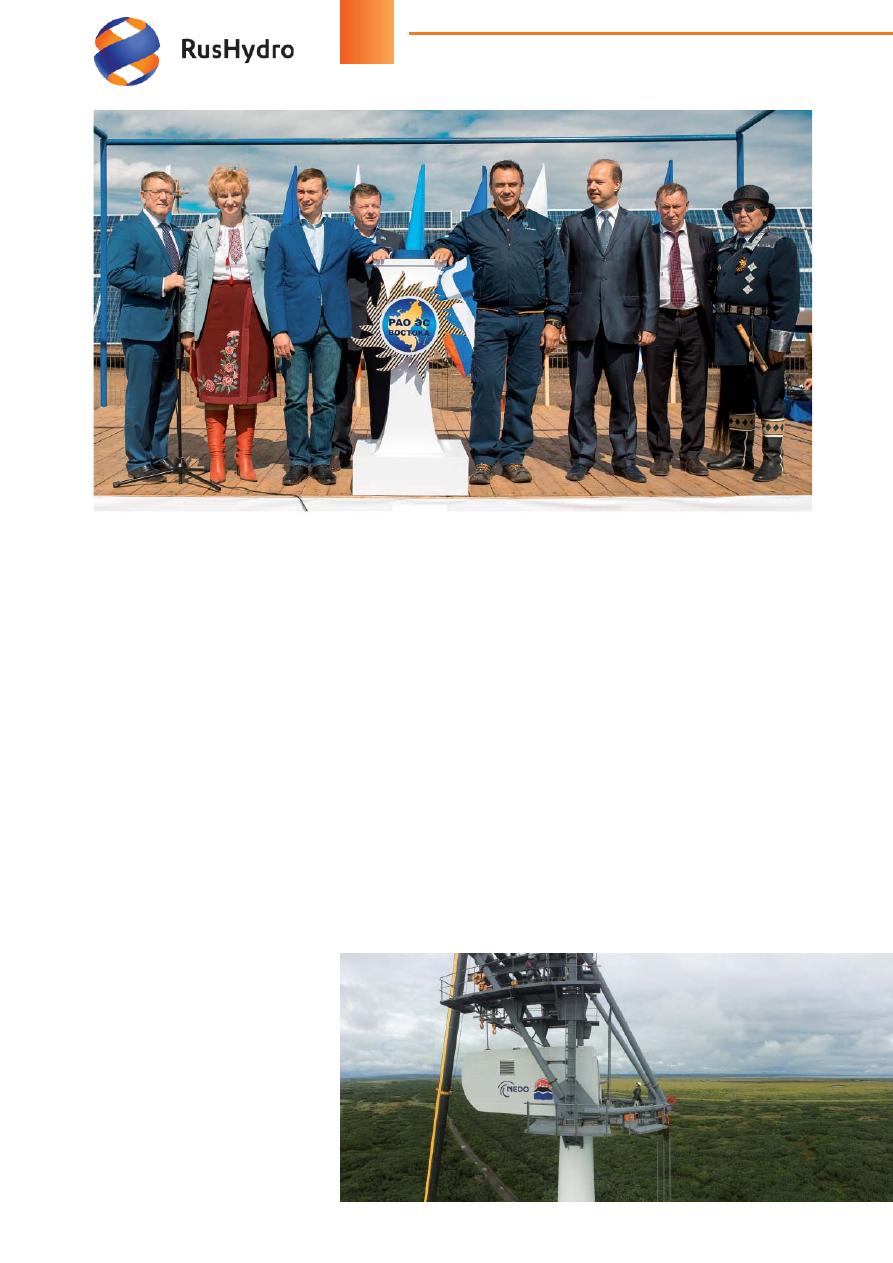
The memorial tablet in honor of
the end of major SPP construction
is erected in the center of Batagay.
The SPP has been of
fi
cially re-
cognized as the world’s northern-
most facility of photovoltaics. The
relevant information is placed in
the Guinnes World Records web-
site. The SPP will be keeping the
leadership among north polar
SPP for a long time. The experi-
ence of Batagay SPP will be ex-
tended to other settlements of nor-
thern Yakutia pretty soon. There
is a plan to construct SPP over
1 MW in Deputatsky, Ust-Kuy-
ga, Zyryanka, Zhigansk, Olenek
settlements.
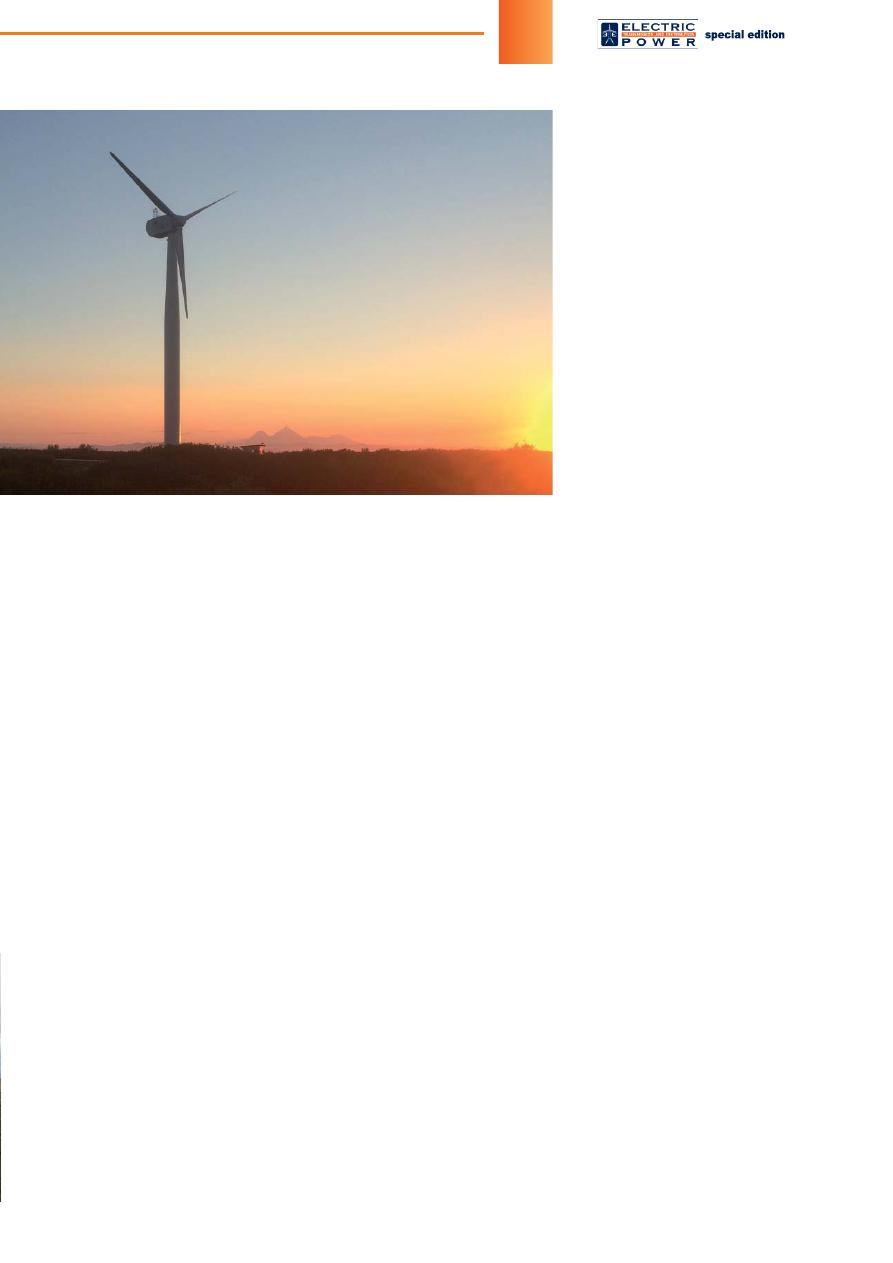
Wind turbine nacelle
erection in Ust-Kamchatsk
village
Wind Turbine
Generators
with Japanese
Temper
Another large-scale project
related to renewable energy was
completed in the north of the Kam-
chatka Region in autumn of 2015.
Wind-driven power plant with elec-
tric capacity more than 1 MW was
built in Ust-Kamchatsk village.
Ust-Kamchatsk residents had
believed until recently, that strong
winds blowing in the village all
year round did only harm. There
were situations in the sixth-largest
populated locality of the Kamchat-
ka Region, when the airport and
the ferry across the Kamchatka
river were closed by reason of
storms. Sometimes even traf
fi
c on
the only road, which ran towards
a regional capital through the cen-
tral valley of the half-island, was
stopped.
The
fi
rst experimental wind-
driven power plant with electric
capacity of 275 KW appeared
in Ust-Kamchatsk in 2013. Start
of a unique international project
was in March 2014. At that time
power engineers of the Far East
and government of the Kamchat-
ka Region entered into a contract
related to renewable energy de-
velopment with New Energy and
Industrial Technology Develop-
Opening of SPP Batagay

61
Wind-diesel power plant
in Ust-Kamchatsk village/
View to Klyuchevskaya Sopka volcano
ment Organization (NEDO) from
Japan. Besides power engineers
of the Far East and government
of the Kamchatka Region have
signed a memorandum with Japa-
nese companies Mitsui & Co. and
Komaihaltec Inc. The subject of
memorandum was integration of
the three wind-driven power plants
(with electric capacity 300 KW
each) into isolated electricity sys-
tem of Ust-Kamchatsk.
Japanese companies con-
sidered that afore-mentioned in-
tegration would be a pilot project
and an opportunity for Research
and Advanced Development.
Equipment was provided free of
charge, in order to test work me-
thods under the condition of of
cold climate. “We had two main
goals, implementing this project
– solving the energy problems of
Ust-Kamchatsk and expansion
of advanced Japanese technolo-
gies”, the chairman of NEDO Kad-
zuo Furukawa explains.
Wind turbines produced by Ko-
maihaltec became a basis of new
wind-driven power plant. The wind
turbines were updated taking into
account the climatic conditions
of the Kamchatka Region. Japa-
nese engineers improved ther-
mal insulation and treated blades
by a special coverage in order to
prevent ice coating and snow ac-
cretion during winter. Wind turbine
nacelle had passed inspection
on the freezing resistance in the
giant refrigerator before it was
sent in Russia. Temperature in the
refrigerator was –40 °C in order
to proof that hydraulic systems
and gear unit were able to ope-
rate under the condition of of cold
weather.
The
fi
rst wind turbine pro-
duced in Japan appeared in the
village in the end of 2014. The
erection of the second and the
third wind turbines were
fi
nished
in September of 2015. Commer-
cial operation of the wind-driven
power plant began in IV quarter
of 2015. Annual electricity output
of the wind-driven power plant is
about 2 million kW•h per year. The
wind-driven power plant in Ust-
Kamchatsk, replacing the DPP
partially, will allow to save more
than 550 tons of fuel. It is signi
fi
-
cant value for the northern village
with 4 thousand residents.
The collection and study of ope-
rational equipment data will have
been going on during the year
since the facility commis
sioning.
Ac cording to Declaration of Inten-
tions, if the pilot project con
fi
rms
the expected commercial ef
fi
-
ciency, the Holding “RAO Energy
Systems of the East” will consider
a possibility of further Japanese
wind turbines expansion in other
isolated areas of the Far East.
“We are interested in expansion
advanced technologies, which will
allow to improve reliability and
security of power supply. We hope
that the project in Ust-Kamchatsk
will be a basis for further
cooperation. Also we believe
that many the same interesting
projects will wait for us”, Alexey
Kaplun says. Next stage of the
wind-driven power plant can
be built on Dembievskaya Spit.
Many
fi
sh-processing factories
are located there. Those factories
are main electricity consumers in
the village. During
fi
shing season
in summertime electric energy
consumption increased in 4 times
on the
fi
sh-processing factories.
The cooperation between Rus-
sia and Japan became a good
example. It was mentioned as
a successful partnership of two
countries during the meeting
between the Prime Minister of
Japan Sindzo Abe and the Presi-
dent of the Russian Federation
Vladimir Putin in May of the cur-
rent year. The cooperation will be
continued in other regions of the
Far East. During Eastern Eco-
nomic Forum (in September of
2015) “RAO Energy Systems of
the East” and Komai Haltec Inc
have signed a memorandum. Ac-
cording to that memorandum,
the companies are going to ana-
lyze the possibility of wind-driven
power plant con
struction with
electric capacity of 1 MW in Tiksi
village of Bulunsky District of the
Republic of Sakha (Yakutia). Also
the Holding “RAO Energy Systems
of the East” and Japanese dis-
tributor of equipment have signed
a memorandum about intentions
to explore an opportunity of wind
turbines production or its separate
units on the Russian territory of the
Far East. Delegates of Japanese
companies have already visited
several companies from Primo-
rye and represented requirements
for manufacturers. The selection
of project participants will be car-
ried out taking into account the
creation of territories of priority
develop ment, as well as a new
customs treatment in Vladivostok.
“I am con
fi
dent that our pro-
gram related to renewable energy

62
development will provide a big
amount of orders for such produc-
tion. During last years, we have
achieved good results in the im-
plementation of renewable energy
facilities in the Far East. At the
moment we should move the nec-
essary equipment production in
the Far Eastern Federal District”,
Alexey Kaplun said.
Expanding
Borders
During the implementation of
renewable energy programs in
the Far East, the Holding “RAO
Energy Systems of the East”
created its own know-how. For
example, wind-diesel power plant
facilities operate successfully in
Novikovo village due to auto matic
control system which was pro-
duced by the Holding companies
during Research and Advanced
Development.
It is not a secret for profes-
sionals that to establish an effec-
tive connection between a renew-
able energy facility and DPP is
a quite dif
fi
cult task. It is related
with a fact that power leaps pro-
duced by wind turbine during
fi
tful wind impact on the electri-
cal power system. Under such
circum stances power engineers
are forced to limit a part of energy
produced by renewable energy
sources in the total power bal-
ance. Automatic control system of
wind-diesel power plant allows to
reduce power leaps in the electri-
cal power system and to manage
by energy sources distributing
electric load between wind-driv-
en power plants and DPP in de-
pendence to changes of electric-
ity consumption in the village and
wea ther conditions.
There are foreign-made auto-
matic control systems of wind-die-
sel power plant, but subsidiaries
of the Holding PJSC “Yakutsk-
energo” and PJSC “Mobile Energy”
were able to develop its own hard-
ware and software complex. Soft-
ware and technical solutions for
frequency maintenance and reac-
tive power compensation of that
hardware and software complex
are know-how. Before the installa-
tion of the automatic control sys-
tem on the constructed wind-die-
sel power plant, the system was
improving by PJSC “Mobile Ener-
gy” for a year. The improvement of
the system was ful
fi
lled by means
of a special experimental model,
where possible emergencies were
simulated. Automatic control sys-
tems of wind-diesel power plant
produced by PJSC “Mobile Ener-
gy” allow to respond on the slight-
est changes of electric energy
generation or consumption.
“Our own automatic control
systems of wind-diesel power
plant allow us to optimize the cost
of all new renewable energy fa-
cilities signi
fi
cantly. In addition,
we do not except the possibility
that the system could be commer-
cially successful in foreign mar-
kets because it could be used for
the installation of renewable en-
ergy sources in isolated systems.
There are no more than six com-
panies in the world, which used
to develop the same intelligent
system of connection. The price of
such systems is millions of dollars.
When we began to develop auto-
matic control systems of wind-
diesel power plant together with
PJSC “Yakutskenergo” we often
faced with incredulous looks. The
system has already passed a test
under actual operation conditions
in Novikov”, CEO of PJSC “Mobile
Energy”, Yuri Mirchevsky states.
Also specialists from compa-
nies of the Holding “RAO Energy
Systems of the East” estimated
results of the various solar panels
operation (there are various types
of solar panels such as monocrys-
tal, polycrystal and thin-
fi
lm) in
order to determine the most con-
venient technology on the Far
East territory.
Place for
Professional
Discussions
Renewable energy develop-
ment program in the Far East,
implemented by “RAO Energy
Systems of the East”, is ful
fi
lled
in cooperation with partners, in-
cluding foreign ones. Owing to
such cooperation a number of new
technologies, engineering solu-
tions and even
fi
nancial resources
come to the Far East.
For example, French company
Helios Strategia won a competition
for the power plant construction
in Batagay. Besides numerous
companies from Germany,
Switzer land, Austria, Korea and
China compete with each other in
order to supply equipment for the
future power plants in the Far East
of Russia. At the same time the
companies “Sakhaenergo” and
“Mobile Energy” adopt experience
of other companies actively and
ful
fi
ll the construction of solar
power plants and wind-driven
power plants by its own efforts.
The international conference
“Renewable Energy Development
in the Russian Far East”, which
took place in Yakutsk in June 2016,
became an excellent discussion
platform for the professionals of
renewable energy area. The event,
organized by the government of
the Republic of Sakha (Yakutia)
together with the Holding “RAO
Energy Systems of the East”, was
attended by over 380 participants
from 14 countries.
Wind-diesel power
plant in Novikovo village
of the Sakhalin Region
63
IMPLEMENTED RENEWABLE
ENERGY PROJECTS
“RAO Energy Systems of the East” put into operation
16 solar power plants and 3 wind-driven power plants in
2012–2016. The implementation of renewable energy
program will save 46 470 tons of diesel fuel annually, or
2.06 billion rubles. Those funds will be used for the return
of investments in renewable energy facilities. Besides those
funds will become an effective tool for control tariffs. The
implementation of renewable energy doesn’t only reduce the
fuel expenses of the company. It will also reduce the subsidies
from the regional budget to the local power engineering after
the payback period of the project. New renewable energy
facilities will replace up to 40% of electric capacity produced
by existing diesel power plants.
Delegates of customers, equip-
ment suppliers, service providers,
regulatory authorities and experts
in the
fi
eld of renewable energy
came together to share experi-
ence and discuss problems and
prospects of alternative energy
develop ment in the region. The
event began with a plenary
meetng “Renewable Energy in the
Far East of Russia: Development
Prio rities and Prospects”. During
the plenary meeting the Repub-
lic of Sakha (Yakutia) head Egor
Bori sov, General Director of “RAO
Ener gy Systems of the East”
Sergey Tolstoguzov and the Swiss
Ambassador in the Russian Fede-
ration Pierre Helg gave a speech.
“Renewable Energy in the Rus-
sian Far East will become a large
trade market in the future and
foreign companies and domes-
tic producers must strive to take
a position there. More and more
companies would like to represent
innovative product samples at our
exhibition and tell about it at the
conference sessions every year.
According to a goal of our event
we strive to represent the best
available technologies to potential
customers and show the modern
requirements of the market to sup-
pliers”, Sergey Tolstoguzov stated,
opening the conference.
Delegates discussed issues of
normative regulation of the indus-
try, project
fi
nancing, and espe-
cially the construction and opera-
tion of renewable energy facilities
in isolated power system under
conditions of extreme climate.
Everyone had a possibility to
visit the exhibition dedicated to
the conference. Yakutsk residents
and guests of the republic had
a chance to see the modern equip-
ment and high technologies. Solar
panels demonstrated operation of
heliostation in the central square of
the city. Besides various technical
innovations and an interactive ex-
hibition were presented there.
Interest of ordinary residents
and investors concerning solar
panels and wind turbines appea-
ring in the Far East shows that
power engineers began to change
shape and economy of the industry
to develop renewable energy.
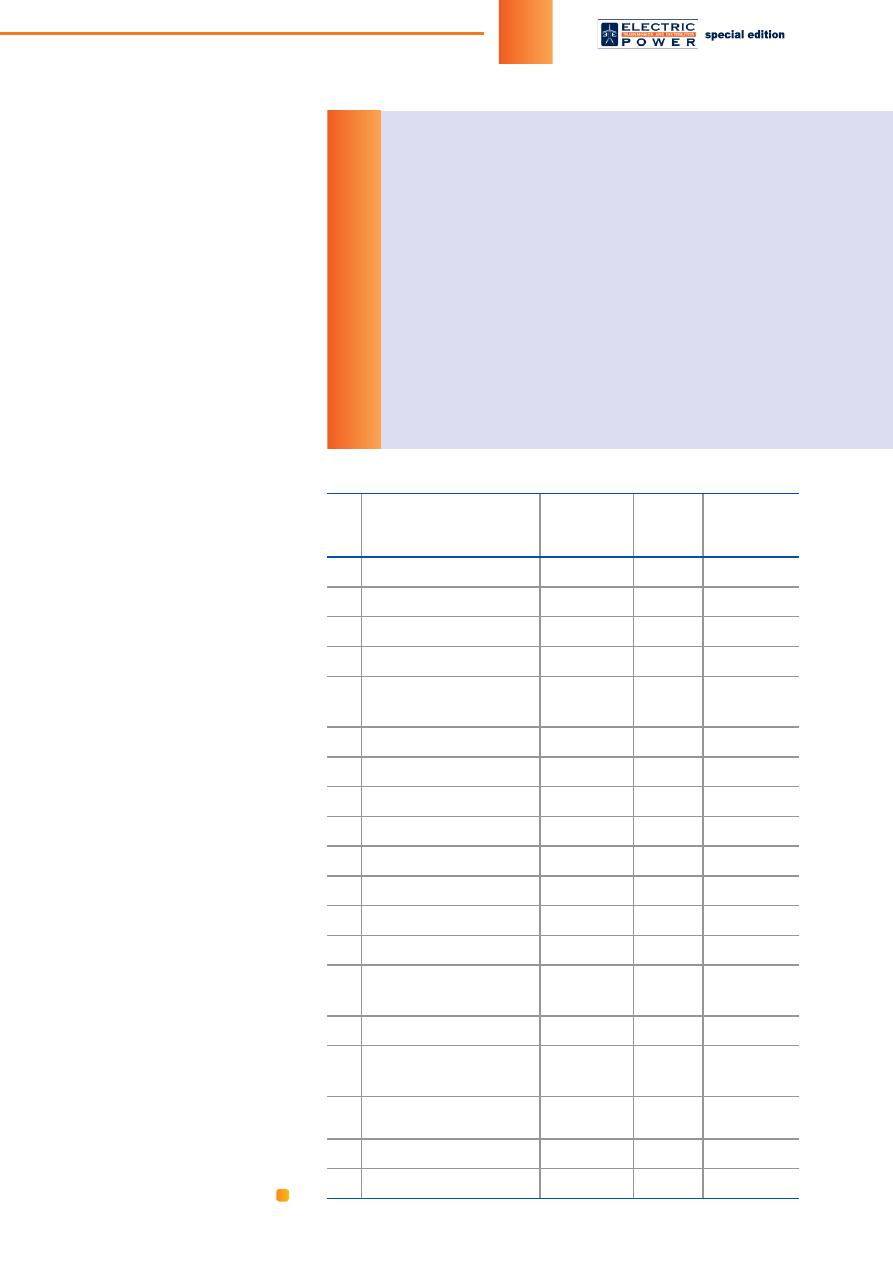
Operating and under-construction facilities of renewable energy
Populated locality
Year of
construction
(* – plan)
Electric
capacity,
KW
Planned fuel
saving,
tons per year
1
SPP Batamay (Yakutia)
2012
60
17.4
2
SPP Yuchyugey (Yakutia)
2012
30
5.9
3
SPP Dulgalah (Yakutia)
2013
20
9.1
4
SPP Kudu-Kyuel (Yakutia)
2013
20
6.5
5
Wind-diesel power plant
Nikolskoye (The Kamchatka
Region)
2013
550
370
6
SPP Kuberganya (Yakutia)
2014
20
6.5
7
SPP Toyon-Ary (Yakutia)
2014
20
7.6
8
SPP Eik (Yakutia)
2014
40
11.9
9
SPP Dzhargalah (Yakutia)
2014
15
5.2
10
SPP Batagay (Yakutia)
2015
1000
300
11
SPP Betenkes (Yakutia)
2015
40
13.3
12
SPP Stolby (Yakutia)
2015
10
3.6
13
SPP Yunkyur (Yakutia)
2015
40
15.7
14
Wind-diesel power
plant Ust- Kamchatsk
(The Kamchatka Region)
2015
1175
533
15
SPP Uluu (Yakutia)
2015
20
7.3
16
Wind-diesel power plant
Novikovo (The Sakhalin
Region)
2015
450
227
17
SPP Verhnyaya Amga
(Yakutia)
2016*
36
25.19
18
SPP Innyah (Yakutia)
2016*
20
8.22
19
SPP Delgey (Yakutia)
2016*
80
24.22
P
owe
r s
y
s
te
m
Оригинал статьи: Sun Goes from the East
The Far East of Russia has become a leader in terms of renewable energy innovations. This is where renewable energy projects have become economically justified today. A long distance between a large number of populated localities and the Unified Power System, as well as the complexity and high price of energy delivery create a huge potential for the optimization of the Far East power engineering by means of adoption of renewable energy technologies.