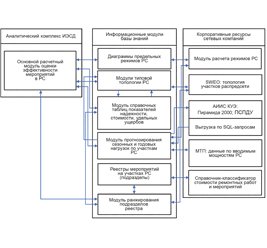
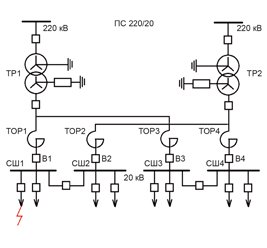
The first-of-its-kind suite of IT-systems designed to control power supply in Sochi was commissioned in September of 2013. Information systems of the Power Supply Control Centre (PSCC) of Sochi energy region were designed according to the special order of JSC “FGC UES”, part of JSC “Russian Grids” Group of Companies.
Главная
Статьи
Статьи по категориям
Innovation Suite of IT-Systems to Control Power Supply of Olympic Venues in Sochi

Innovation Suite of IT-Systems to Control Power Supply of Olympic Venues in Sochi
HTML-версия
Andrey BADALOV, First Deputy General Director, Dmitry GVOZDEV, Deputy General Director, Cand. of Technical Sciences, Boris SHVEDIN, Chief Ontologist, Cand. of Psychological Sciences, CJSC “RTEC”, Leonid BUZAEV, Deputy Chief Engineer, JSC “FGC UES
Special issue “ELECTRIC POWER. Transmission and Distribution” for the World Smart Energy Week (Tokyo, Japan), February 2014