The MAIN JOURNAL for POWER GRID SPECIALISTS in RUSSIA
3 - 6 J U N E 2 0 1 9
MADRID, SPAIN
The MAIN JOURNAL for POWER GRID SPECIALISTS in RUSSIA
3 - 6 J U N E 2 0 1 9
MADRID, SPAIN

22
Experience оf Smart Grid Implementation
for Operation Сosts Optimisation
of Distribution Power System
Dmitriy SHAROVATOV,
BESK JSC
Andrey KUCHERIAVENKOV,
Trinity Engineering LLC
ANTRAKS R&D, LLC
+7 (495) 991-12-30,
www.antraks.ru,
offi ce@antraks.ru
N
owadays half of World's population is living
in the cities. According to the forecasts ur-
ban population will reach 60% by the 2030.
Successful city growth is highly depend on its
energy system growth and improvement. Russian inno-
vative energy company BESK, who owns transmission
and distribution power grids 0.4 to 500 kV implements
complex renovation of the energy system based on
Smart Grid principles during last 3 years.
Prior the project start Ufa city power distribution grid
had a lot of system issues prevented it's eff ective growth
like: usage of old and outdated equipment (the equip-
ment was mainly mounted in 1970-1980), unsystematic
building of the grid and signifi cant load increase (up to
1/3 of total regional power capacity). City population
and territory growth makes it harder to get operational
access to the grid facilities while intensive construction
inside existing areas causes demand to increase grid
capacity without building of new power supply facilities
as there is no space for them. To select the required set
of power grid control and monitoring base technologies
which should be implemented (claimed as Smart Grid
in total) it was taking in account specifi c characteristics
of Ufa city power system as well as forecast information
regarding its future development.
DEFINITION OF MODERNIZATION CRITERIA
According to the project feasibility study one of the most
important concepts was to provide full network observ-
ability and manageability by renovate no more than 25%
of substations. That's why it was important to range
overall grid facilities such as substations and cable pow-
er lines by renovation priorities. First of all, criteria for
providing substations with remote control and remote
monitoring was defi ned. The criteria was required for
SmartGrid model. Then equipment renovation order
prio rities were set.
Priorities for substation remote control:
1. All distribution substations.
2. Transformer substations, where a network division
points are located (normal breaks).
3. Transformer substations, which have two or more
branches with other transformer substations.
4. Transformer substations that signifi cantly aff ect the
power supply of particularly important consumers.
5. Transformer substations located in the transmission
networks which are the most important for operational
and technical management.
Priorities for substation remote monitoring:
1. All distribution points and transformer substations pro-
vided with remote control.
2. All new substations and substations which will be re-
novated or rebuilt.
3. Other transformer substations where observability is
signifi cant (typically it should be one observable for
each two-three no observable).
Priorities of equipment renovation order:
1. Meeting the requirements from the System operator
about the amount of power involved in the temporary
shutdown schedule.
2. Elimination of the network overload, reliable commu-
nication channels organization.
3. Reliable power supply for consumers from the fi rst
power supply reliability category (health facilities, child
care facilities, control centres etc.).
This chronological priority order of equipment reno-
vation allows energy company to provide high power
system reliability during the project execution and after
its completion.
FINE-TUNING TECHNOLOGIES
IN PILOT PROJECT
The test of selected approach under conditions of target
system and the creation of the basic foundations of pilot
project modernization were initiated in May 2014. The
scope of the pilot project included:
– renovation and automation of power grid section
consists of two distribution substation and fi ve trans-
former substations (according to full project it should
be renovated about 500 substations in total);
– construction of power grid control centre in Ufa city;
– establishment of intelligent commercial power me-
tering system in pilot region.
PCI Control automated dispatch control system be-
came the core of Network management centre of the
BESK. Reconstruction of distribution points and trans-
former substations included replacement of the old and
worn-out switching units to new ones, replacement of
measuring current and voltage transformers with ad-
vanced devices and also transferring the data to electric-
ity generation facilities in normal or emergency modes
to Network management centre.
Signifi cant contribution to electric system reliability
improvement and minimization of emergencies during
the pilot project was made by network optimization
during connection of new clients. Previously observed
SMART GR
I
D
23
network overload had disappeared and replacing over-
head power line sections with cable ones allowed to im-
prove the insulation.
Replication of pilot project proven solutions is cur-
rently applied in the entire Ufa city electric system. The
plan of transition from current condition to SmartGrid
target model is designed for 5 years and includes the
following: reconstruction and automation of 513 distrib-
uting points and transformer substations for ensuring
their controllability and observability, network structure
optimization (installation 100 km of cable lines) and also
installation more than 80,000 metering devices.
As a result of this, Smart Grid pilot project level of
commercial power losses was decreased by 96.3%:
from 27.3% to 1% (about 500,000 rubles). According to
the results of the successful pilot project, the estimations
obtained on the stage of feasibility study were correct.
ENSURING SYSTEM OBSERVABILITY
Implementation of the functions specifi ed in feasibility
study has required substantial increase the amount of
normal mode data as well as emergency mode data.
Normal mode data included the traditional set:
– switch positions (circuit-breakers, draw-out ele-
ments, earthing blades, jumpers);
– current mode parameters for each connection (cur-
rent, power, quantity of electric energy) and param-
eters common for all sections (voltage, frequency
etc.).
According to the results of the pilot project, diffi culties
of the transformer substations observability were un-
derstood. Practical tests of devices from three diff erent
manufacturers (Germany and Russia) have shown that
devices identifi cation of phase-to-ground short circuit
direction as well as of double- and triple-phase short cir-
cuits and double and triple line-to-ground short circuits
plays critical role. According to this, feeder monitoring
devices performance was improved.
On the basis of more sensitive device manufactured
in Russia by A-signal which determines the direction of
emergency processes with current of more than 0.5 A,
new-generation device which can precisely determine
very short-term network processes was developed. Net-
work consisting of such devices can collect the data of
residual fault current and transfer it into the cloud sys-
tem which performs correlation analysis and precisely
detects emergency area. Versatile distributed network of
de veloped feeder monitors with intellectual cloud comput-
ing might help not only to detect the emergency area but
also, in some cases, to predict this process and needs in
network equipment maintenance. Cost of each measur-
ing point was reduced during the development stage.
Application of the specialized feeder monitor “A-sig-
nal” devices ensured the increased amount of emergency
data on each feeder – short-circuit current, damage type
(PTP, PTG), failed phase, fail direction. Such data content
allows engineers to signifi cantly reduce duration of emer-
gency areas detection and respectively to substantially
improve key SAIDI and SAIFI indicators.
Practical test of A-Signal devices capabilities included:
– double- and three-phase short circuits between
phases;
– phase-to-ground short-circuits;
– phase-to-ground short circuits in diff erent feeders.
At the present time during Smart Grid project implemen-
tation on the reconstructed distributing points and trans-
former substations integration of supervisory system with
upgraded feeder monitoring devices is being performed.
Now there is a capability of network overload rapid
identifi cation, changing of network diagram, performing
of scheduled and post-emergency switchings. Operating
costs on reconstructed facilities were reduced due to in-
stallation of plug and play equipment.
Р
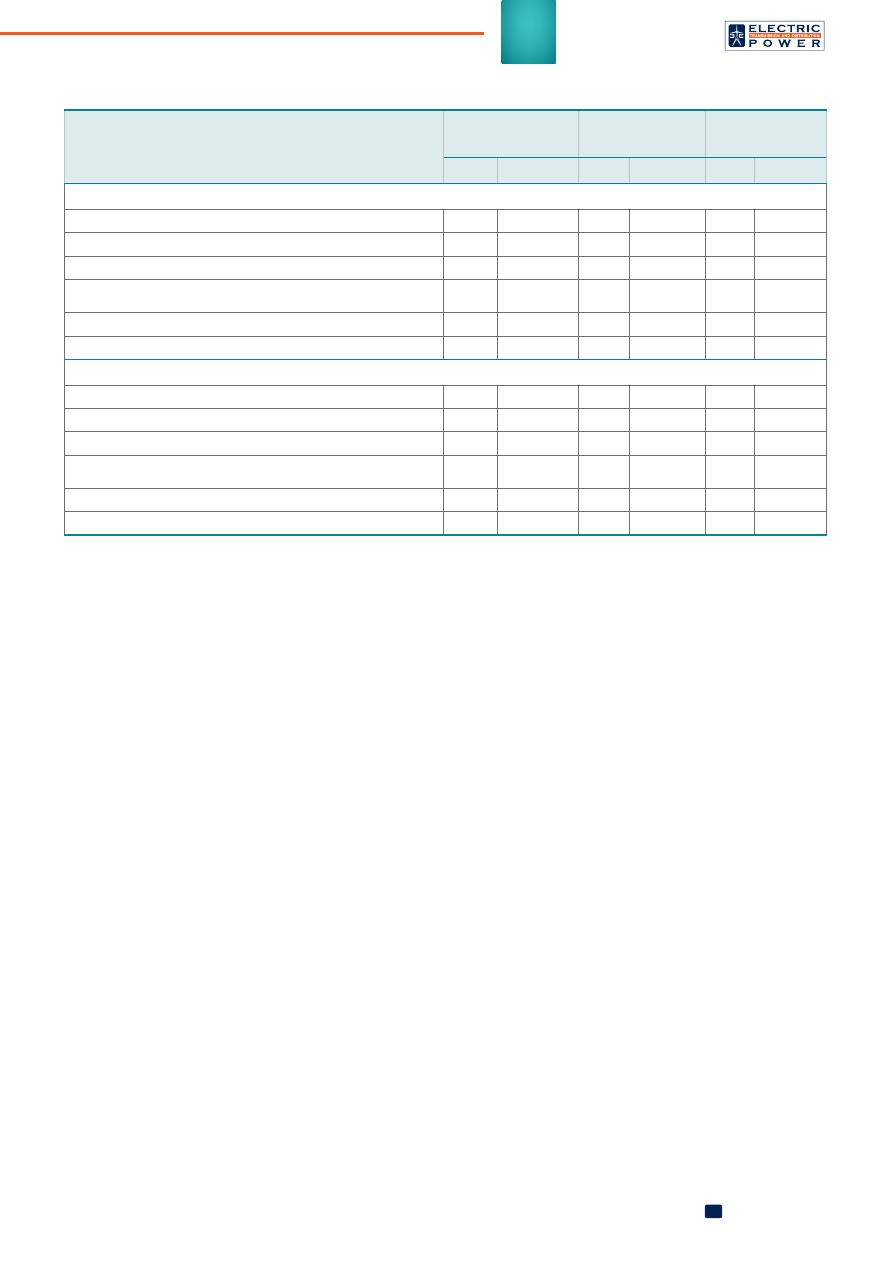
Comparison of feeder monitors from diff erent manufacturer
Indicator
Sicame FCM,
Siemens
IKI-50, Kries-
Energietechnik
A-signal,
Antraks
En. CL Non en. CL En. CL Non en. CL En. CL Non en. CL
Insulated neutral
Double- and three-phase short circuits identifi cat.
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Double- and three-phase short circuits direction identifi cat.
No
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Double- and three-phase ground return short circuits identifi cat.
Yes
No
Yes
No
Yes
Yes
Double- and three-phase line-to-ground short circuits direction
identifi cat.
No
No
Yes
No
Yes
Yes
Single line-to-ground short circuits identifi cat.
No
No
Yes
No
Yes
Yes
Single phase-to-ground short circuits direction detection
No
No
Yes
No
Yes
Yes
Compensated neutral
Double- and three-phase short circuits identifi cat.
No
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Double- and three-phase short circuits direction identifi cat.
No
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Double- and three-phase ground return short circuits identifi cat.
No
No
Yes
No
Yes
Yes
Double- and three-phase line-to-ground short circuits direction
identifi cat.
No
No
Yes
No
Yes
Yes
Single line-to-ground short circuits identifi cat.
No
No
Yes
No
Yes
Yes
Single phase-to-ground short circuits direction detection
No
No
Yes
No
Yes
Yes
The 25th CIRED Session
Special issue, June 2019
Оригинал статьи: Experience оf Smart Grid Implementation for Optimization of the Distributive Electric System Operation Expenses
Nowadays half of World’s population is living in the cities. According to the forecasts urban population will reach 60% by the 2030. Successful city growth is highly depend on its energy system growth and improvement. Russian innovative energy company BESK, who owns transmission and distribution power grids 0.4 to 500 kV implements complex renovation of the energy system based on Smart Grid principles during last 3 years.